
A. The Philippines
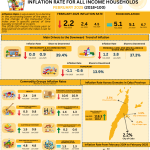
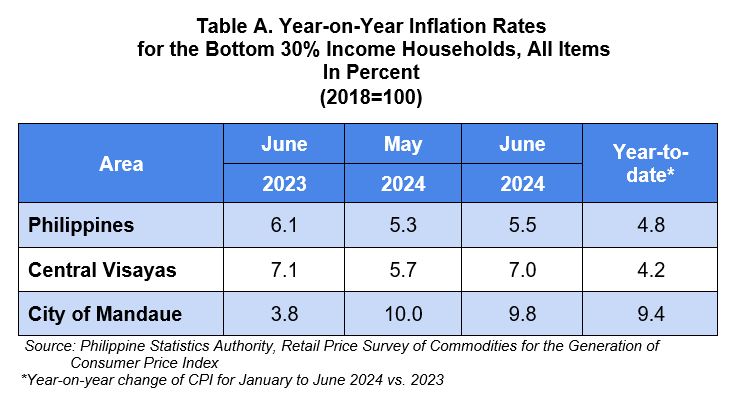
The country’s inflation rate for the bottom 30% income households increased to 5.5 percent in June 2024 from 5.3 percent in May 2024. This brings the average inflation for this income group from January to June 2024 to 4.8 percent. In June 2023, inflation rate was posted at 6.1 percent. (Table A)
B. Central Visayas
1. Regional Inflation
Following the trend at the national level, inflation rate for the bottom 30% income households in Central Visayas increased to 7.0 percent in June 2024 from 5.7 percent in May 2024. The region’s average inflation for this income group from January to June 2024 stood at 4.2 percent. In June 2023, the inflation rate in the region was higher which recorded at 7.1 percent. (Table A)
C. City of Mandaue
1. Headline Inflation
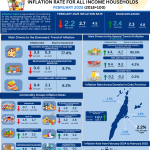
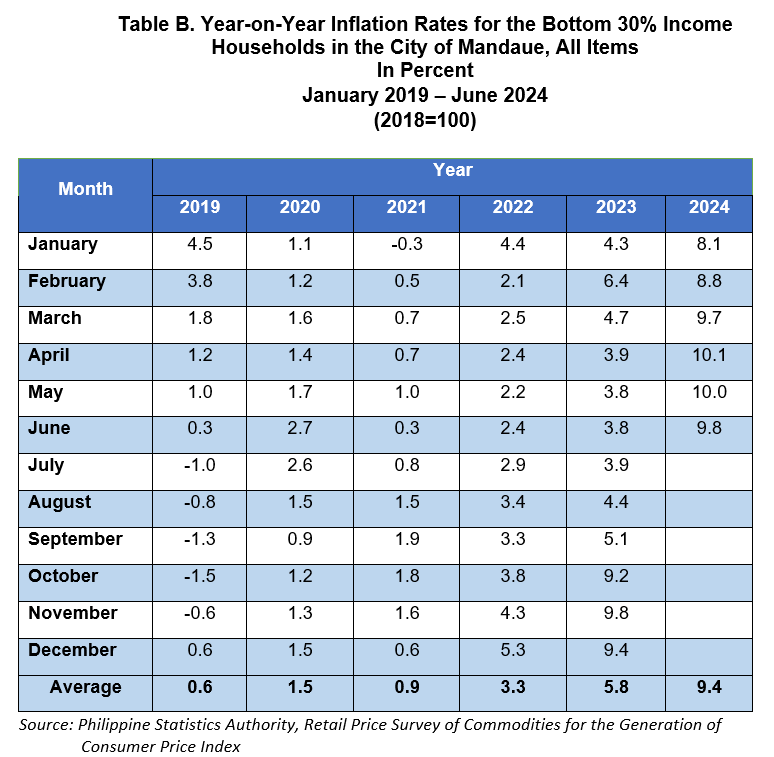
The headline inflation rate for the bottom 30% income households in the City of Mandaue had a slower increase at 9.8 percent in June 2024 from 10.0 percent in May 2024. This brings the city’s average inflation at 9.4 percent from January to June 2024. In June 2023, the inflation rate was lower which recorded at 3.8 percent. (Table A and Figure 1)
1.1 Main Drivers to the Downward Trend of Headline Inflation in the City of Mandaue
The main drivers to the deceleration of the headline inflation rate during the month were mainly brought by the slower year-on-year increases of food and non-alcoholic beverages at 8.4 percent, personal care, and miscellaneous goods and services at 4.4 percent, and health at 6.2 percent from their respective inflation rates at 8.9 percent, 12.8 percent, and 8.1 percent in May 2024. (Table 3)
In addition, slower annual increments were also recorded in the indices of transport at 3.4 percent, clothing and footwear at 0.9 percent, and alcoholic beverages and tobacco at 11.2 percent during the month from their respective inflation rates at 4.0 percent, 1.0 percent, and 11.3 percent in May 2024. (Table 3)
On the other hand, faster annual increases were posted during the month in the indices of housing, water, electricity, gas and other fuels at 24.4 percent, and furnishings, household equipment and routine household maintenance at 3.8 percent from their respective previous month’s inflation rates at 23.2 percent and 3.5 percent. (Table 3)
Moreover, the indices of commodity groups that retained their previous month’s inflation were as follows:
a. Information and communication, 0.0 percent;
b. Recreation, sport and culture, 22.5 percent;
c. Education services, 0.0 percent;
d. Restaurants and accommodation services, 0.9 percent; and
e. Financial services, 0.0 percent. (Table 3)
1.2 Main Contributors to the Headline Inflation
The following commodity groups were the top three contributors to the June 2024 overall inflation for the bottom 30% income households in the City of Mandaue:
a) Housing, water, electricity, gas and other fuels with 51.0 percent share or 5.0 percentage points.
b) Food and non-alcoholic beverages with 39.1 percent share or 3.8 percentage points; and
c) Transport with 2.1 percent share or 0.2 percentage point.
2. Food Inflation
Food inflation rate for the bottom 30% income households in the City of Mandaue had a slower annual increase at 9.0 percent in June 2024 from 9.5 percent in the previous month. In June 2023, the food inflation stood at 5.6 percent. (Table 7)
2.1 Main Drivers to the Downtrend of Food Inflation
The downtrend in the food inflation was primarily driven by the faster year-on-year decrease of fish and other seafood at 11.7 percent in June 2024 from 8.1 percent annual drop in May 2024. Also contributed in deceleration of the food inflation was the faster annual decrease of milk, other dairy products and eggs at 3.7 percent in June 2024 from 0.5 percent annual increase in May 2024.The third main source of the food inflation was the slower annual increase of meat and other parts of slaughtered land animals at 4.8 percent in June 2024 from 5.8 percent in the previous month. (Table 5)
Additional lower inflation rates were also noted in the indices of the following commodity group during the month:
a. Fruits and nuts, 17.2 percent from 20.4 percent;
b. Sugar, confectionery and desserts, -7.5 percent from -6.2 percent; and
c. Flour, bread and other bakery products, pasta products, and other cereals, 1.3 percent from 1.7 percent. (Table 5)
In contrast, higher inflation rates were observed in the indices of the following commodity during the month:
a. Corn, 6.7 percent from -9.4 percent;
b. Vegetables, tubers, plantains, cooking bananas and pulses, 38.7 percent from 36.5 percent; and
c. Ready-made food and other food products, 11.2 percent from 9.9 percent. (Table 5)
Moreover, no movement for the index of oils and fats, while rice retained its previous month’s inflation rate at 21.9 percent. (Table 5)
2.2 Main Contributors to the Food Inflation
Food inflation contributed 38.2 percent or 3.7 percentage points to the June 2024 overall inflation for this particular income group.
Among the food groups, the main contributors to the food inflation during the month were the following:
a. Cereals and cereal products, which includes rice, corn, flour, bread and other bakery products, pasta products, and other cereals, with 86.3 percent share or 7.8 percentage points;
b. Vegetables, tubers, plantains, cooking bananas and pulses with 20.5 percent share or 1.8 percentage point; and
c. Meat and other parts of slaughtered land animals with 7.2 percent share or 0.7 percentage point.
TECHNICAL NOTES
The Philippine Statistics Authority generates and announces the monthly Consumer Price Index (CPI) based on a nationwide survey of prices for a given basket of goods and services. Two important indicators, the inflation rate and purchasing power of the peso (PPP), are derived from the CPI which are important in monitoring price stability and the value of the country’s currency.
The CPI is an indicator of the change in the average retail prices of a fixed basket of goods and services commonly purchased by households relative to a base year.
Retail Price is the price at which a commodity is sold for spot in small quantities for consumption.
Base Period/Base Year is the period, usually a year, at which the index number is set to 100. It is the reference point of the index number series.
Market Basket is a term used to refer to a sample of goods and services that are commonly purchased and bought by an average Filipino household.
Weight is a value attached to a commodity or ground of commodities to indicate the relative importance of that commodity or group of commodities in the market basket.
Inflation Rate is equivalent to a decline in the purchasing power of the peso. It is the change in the CPI over a specific period of time (usually a month or a year). That is,
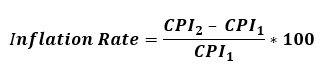
where:
CPI1 - is the CPI in the previous period
CPI2 - is the CPI in the current period
The Purchasing Power of the Peso (PPP) is a measure of the real value of the peso in a given period relative to a chosen reference period. It is computed by getting the reciprocal of the CPI and multiplying the result by 100. That is,
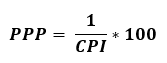
Headline Inflation is the rate of change in the weighted average prices of all goods and services in the CPI basket.
Approved by:
MELCHOR B. BAUTISTA
Chief Statistical Specialist
LGCS/MJDG