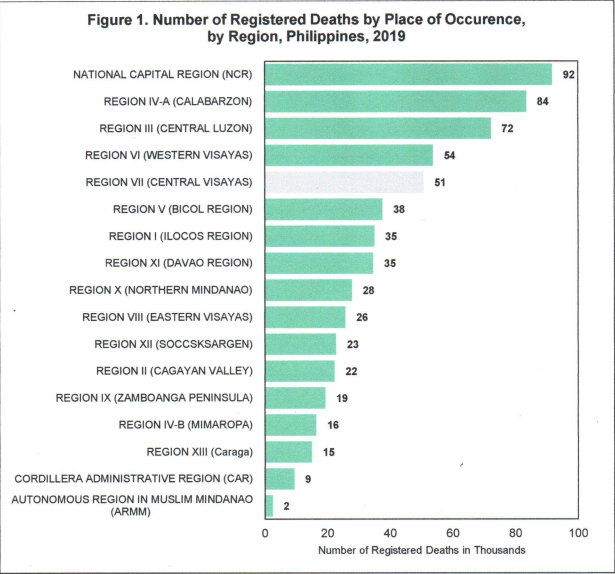
8.16% deaths are registered in Central Visayas
Central Visayas registered a total of 50,651 registered deaths, this comprises 8.16% of the total registered deaths (620,414) in the Philippines for the year 2019. The region ranked 5th in terms of the highest number of deaths recorded in 2019. (See Figure 1.)
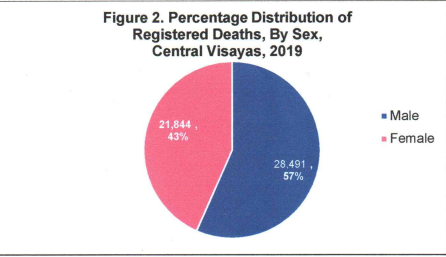
More males died than females
In 2019, there were more male registered deaths with 28,491 or 57% compared to female deaths with 21,884 or 43% of the total registered deaths in the region. This resulted to a sex ratio of 130 males for every 100 females. (See Figure 2)
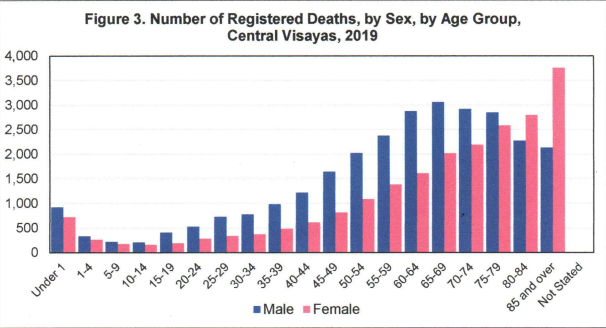
More males died at the age of 65-69 years old
In 2019, death registered for age group 65-69 had the highest among males with 3,063 or 10.75% to the total male registered deaths in Central Visayas. On the other hand, female deaths registered highest at age group 85 and over with 3,757 or 17.20% to the total female registered deaths. (See Figure 3.)
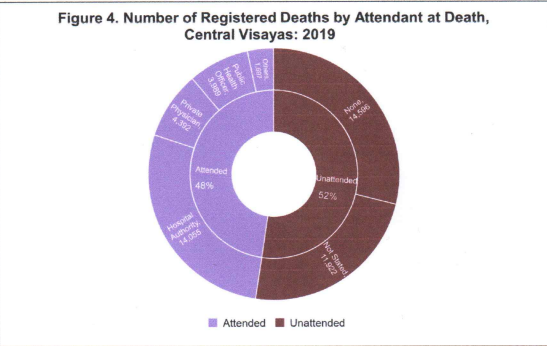
Fifty-two percent of registered deaths are unattended
Of the total registered deaths in Central Visayas, 52% or 26,518 number of registered deaths were unattended for the year 2019 while 48% or 24,133 were attended by either hospital authority with 14,055 or 27.7%, Private Physician with 4,392 or 8.7%, Public Health Officer with 3,989 or 7.9%, and others with 1,697 or 3.4%. (See Figure 4.)
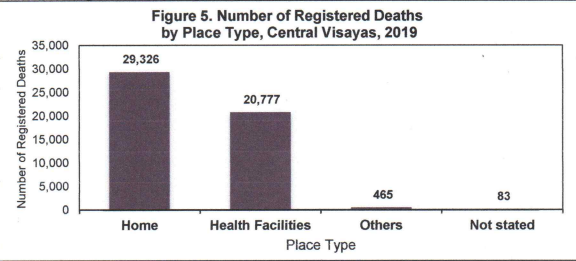
Larger percentage of deaths took place in their own homes.
In Central Visayas, 58% or 29,326 registered deaths took place at home and 41% or 20,777 registered deaths took place at Health Facilities. An indicative that there are more unattended deaths were registered. (See Figure 5.)
Highest registered deaths occurred in Cebu province
Among the provinces in Region 7, Cebu province had the highest number of registered deaths recorded in Central Visayas 2019 with 15,489 or 30.6%. Followed by the province of Bohol, Negros Oriental and Siquijor with 9,375 or 18.5%, 9,325 or 18.4% and 772 or 1.5% respectively. Of the three highly urbanized cities of region 7, Cebu City had the highest number of registered deaths with 12,268 or 24.2% followed by Mandaue City and Lapu-Lapu City with 1,737 or 3.4% and 1,685 or 3.3% respectively from the total number of registered deaths in Central Visayas. (See Figure 6.)
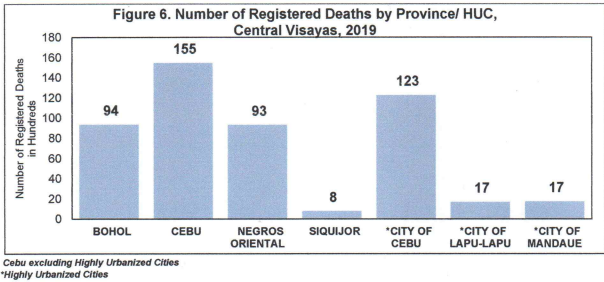
Cebu excluding Highly Urbanized Cities
*Highly Urbanized Cities
Infant, Fetal and Maternal Deaths in Central Visayas
In Central Visayas, a total of 1,644 number of registered infant deaths were recorded. This contributed to 3.26% from the total number of registered deaths in the region. There were 919 fetal deaths and 158 maternal deaths which contributes to 1.82% and 0.31% from the total number of registered deaths respectively. (See Figure 7)

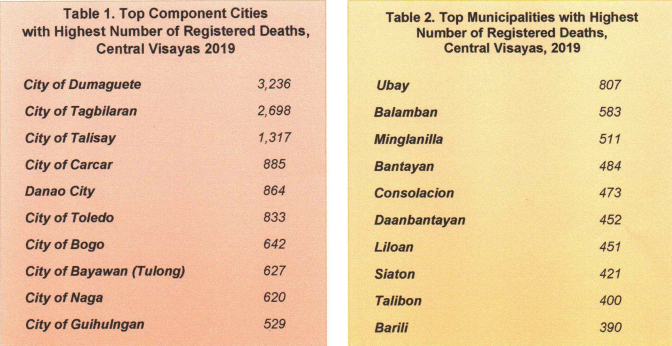
Below are the top component cities and municipalities with highest number of registered deaths in Central Visayas, 2019. (See Table 1 and 2)
Technical Notes:
Vital statistics » are derived from information obtained at the time when the occurrences of vital events and their characteristics are inscribed in a civil register. Vital acts and events are the births, deaths, fetal deaths, marriages, and all such events that have something to do with an individual's entrance and departure from life together with the changes in civil status that may occur to a person during his lifetime.
Death » refers to the permanent disappearance of all evidence of life at any time after live birth has taken place.
Maternal Death » is the death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of the pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management but not from accidental or incidental causes.
Infant Death » are deaths that occurred before reaching age 1.
Fetal Death » is a death prior to the complete expulsion or extraction from its mother of a product of conception, irrespective of the duration of pregnancy; the death is indicated by the fact that after such separation the fetus does not breathe or show any other evidence of life, such as beating of the heart, pulsation of the umbilical cord, or definite movement of voluntary muscle.
Place of Usual Residence » refers to the place where the person habitually or permanently resides.
Place of Occurrence » refers to the place where the vital event took place.
Approved by:
(Sgd.) ARIEL E. FLORENDO
Regional Director

